A parallel process breaks down silos and barriers that hinder content creation and constrain collaboration.
Learn how adopting a parallel approach facilitates simultaneous work and dynamic communication to deliver greater productivity and faster development times.
Serial vs Parallel Process
Search for ‘Serial vs. Parallel Process’ and you’ll find thousands of articles talking about one particular study; Serial vs Parallel Processing: Sometimes They Look Like Tweedledum and Tweedledee but They Can (And Should) be Distinguished.
James T. Townsend's work highlights the importance of distinguishing between these two modes of processing:
- Serial Processing involves developing content sequentially, one step at a time. Think of this as working through a checklist, item by item.
- Parallel Processing involves developing multiple pieces of content simultaneously. Think of this as multitasking, or handling several tasks at once.
Working in-parallel offers several advantages over a sequential approach, including completing multiple tasks concurrently to reduce overall development timelines.
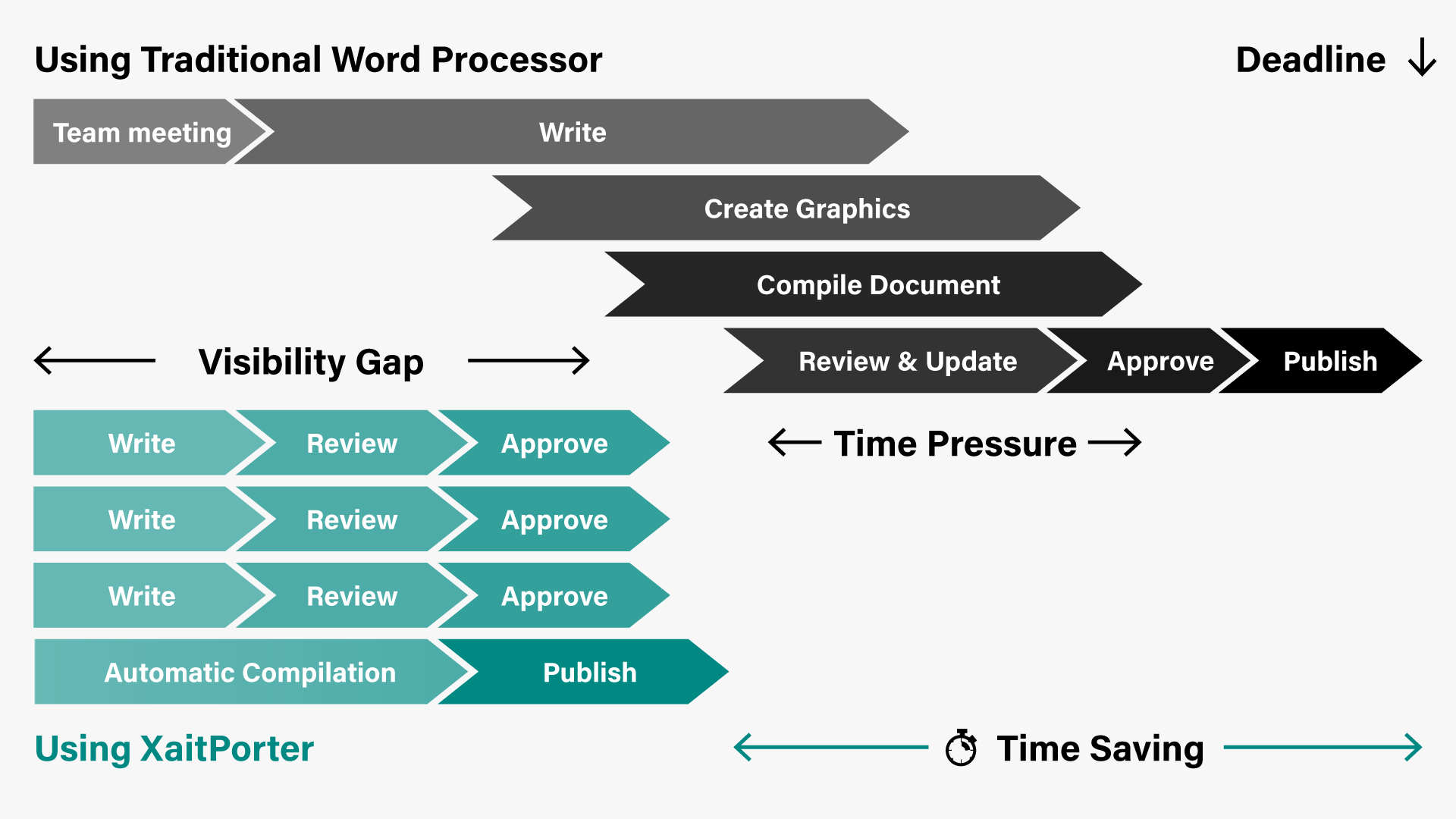
Traditional Document Creation Process
Document creation is a detailed and intricate process, and rightly so. Every winning proposal, flawless legal document, or detailed report, requires many hands. The process you choose coordinates those hands.

While following a serial process, step-by-step, can be more straightforward to manage, it can also be time-consuming. Not exactly a perk when it comes to large, complex documents and tight deadlines.
In the traditional approach to document creation, the process resembles a serial assembly line. One expert writes a portion and passes it to the next expert, who writes their share. They pass it on to the next expert, and so forth. The process stalls for review and then kicks-off again, repeating until the document is complete or it's due, whichever comes first.
Not only is this time-consuming, it is also prone to errors, omissions, and redundant effort.
Simultaneous Document Creation
Now, imagine this: a solution architect and a writer are working on a proposal together. As the architect responds to technical requirements, the writer is creating the story around the solution’s outcomes and benefits.
The content evolves rapidly, with each contributor building on the other. At the same time, reviewers weigh in with their thoughts. A lively discussion ensues, with different perspectives and innovations until the team comes to consensus and completes the document.
This dynamic, real-time collaboration leads to a more accurate, insightful, and compelling proposal, faster.
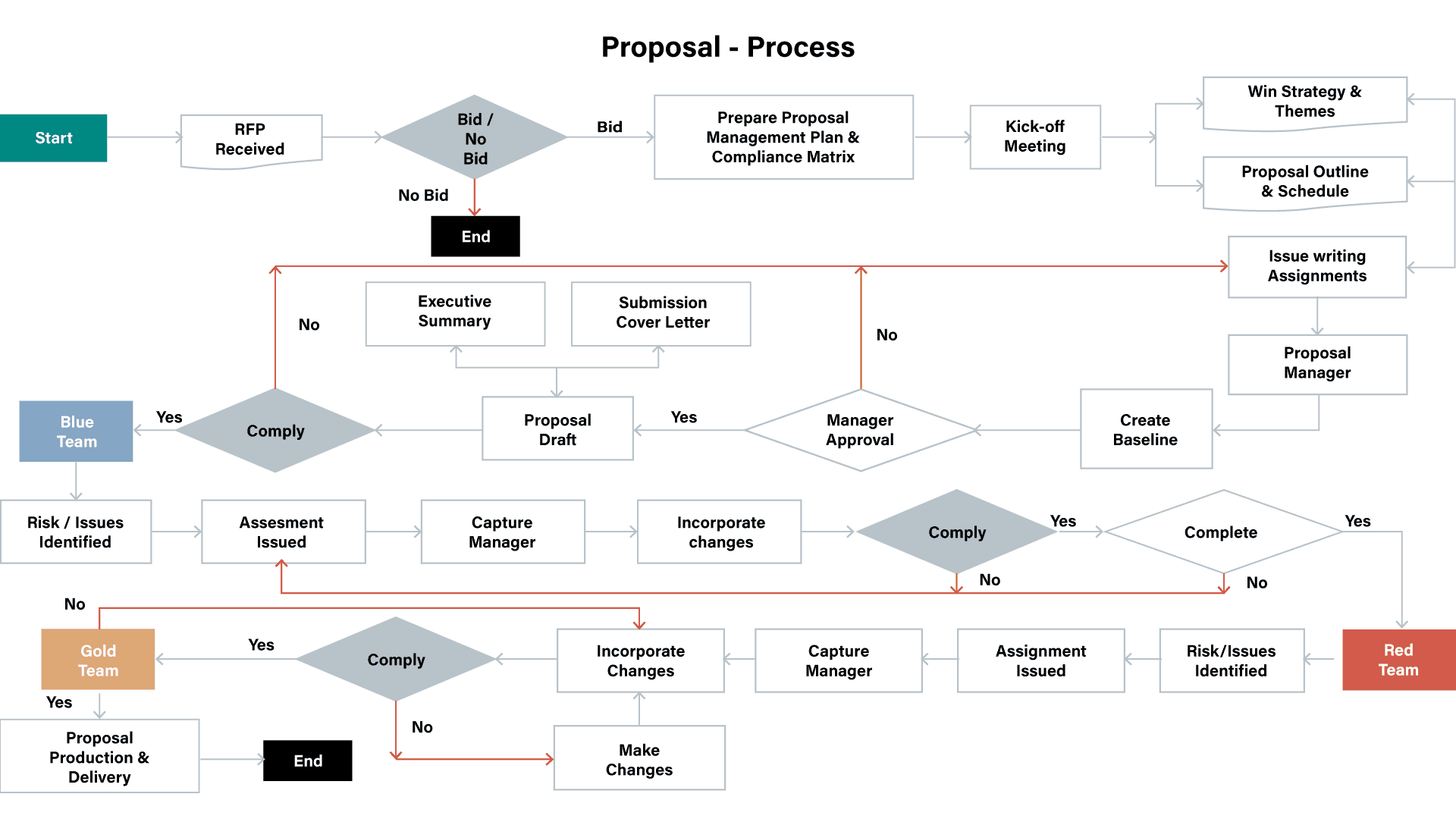
How it Works
A parallel process involves working on multiple tasks simultaneously. For example, multiple experts working on the same document at the same time. Everyone can see what’s changed real-time, while review feedback drives continuous improvement. This approach significantly accelerates development time and improves overall content quality.
How it works:
- Multiple writing tasks begin at the same time in the same document.
- Multiple individuals work on different tasks simultaneously in the same document.
- Continuous improvement is rapid as feedback is received and added real-time.
- Tasks are completed faster with more in-depth, higher-quality content.
Suggested Content


Complex Document Management: How to Write and Manage Complex Documents
December 12, 2024
Benefits
A parallel process offers several advantages over a serial, or sequential approach. By adopting a parallel approach, organizations:
- Accelerate Timelines: Multiple tasks are performed concurrently, optimizing resources and cutting turnaround time (TAT) by half or more.
- Improve Quality: Experts write together, playing off each other’s strengths to deliver more comprehensive content and value for the readers.
- Optimize Reviews: Reviewers work as a team, side-by-side with writers for a real-time feedback loop that reduces questions and expedites improvements.
- Improve Engagement: Simultaneous work boosts communication and knowledge sharing that drives consistency and accuracy.
- Adapt and Grow: A parallel process makes teams more agile and adaptable to change, including amendments and increasing volume.
Choosing the Right Approach
The decision to use a serial or parallel process depends on several factors. By carefully considering these factors, you can select the best approach to optimize your document development process.
You might effectively use a serial approach to deliver:
- Simple Projects: For smaller, less complex projects with clear dependencies, a serial approach might be sufficient.
- Highly Specialized Documents: When projects require a specific siloed expertise, a sequential approach may be adequate.
However, a parallel process is recommended when collaborating on:
- Complex Projects: For large, complex projects, with multiple tasks, expertise, and dependencies, a parallel approach significantly boosts content quality.
- Time-Sensitive Projects: When deadlines are tight, a parallel approach eliminates manual effort and errors to significantly expedite writing.
- Large Documents: When working on large, complex documents, a parallel process facilitates more efficient resource allocation to optimize productivity.
- Collaborative Projects: When multiple experts need to work together on different aspects of a project, a parallel approach fosters more efficient communication.
The Parallel Process Advantage
Modern co-authoring tools like XaitPorter empower an efficient parallel process, regardless of location or time zone. Advanced features, including automation, workflow, version control, and dynamic reviews make it the ideal solution for enterprise organizations seeking to streamline their process and optimize their expert resources.
In fact, XaitPorter teams write large, complex documents 70% faster with:
- Real-time Co-authoring: Any number of users work on the same document at the same time, without overwriting, while seeing each other's changes as they happen.
- Auto Save and Version Control: Work is automatically saved, audit trails and version control tracks changes, and users can compare iterations and revert to previous versions.
- Document Control: Granular, task-based access controls what users can do with documents, protecting information, especially sensitive or confidential data.
- In-Document Commenting: Centralized feedback and discussions within the document, as well as user tagging, facilitates communication and context.
- Automation: Automation and workflow eliminates manual coordination and effort, including formatting, to streamline the process and save significant time.
- AI-Powered Content Library: Makes leveraging existing content easy while providing relevant suggestions to expedite writing.
- Integration: Seamless integration with other productivity tools, such as CRM and CPQ make using accurate and consistent information easy.
The choice between serial and parallel process can significantly impact your efficiency and quality. By leveraging modern computing technology to embrace a parallel process, you can eliminate manual effort, save time, and do more with your same staff.